Hair loss is a common concern affecting both men and women at various stages of life. This condition can stem from multiple factors, including medical conditions, environmental influences, and lifestyle choices. To better comprehend this phenomenon and identify effective hair loss treatments, let's delve into the primary causes of hair loss and the strategies to combat it effectively.
Top Causes of Hair Loss
1. Health conditions that can trigger Hair Loss
Certain medical conditions can cause hair loss, resulting in partial or complete hair shedding depending on the situation. The most common include:
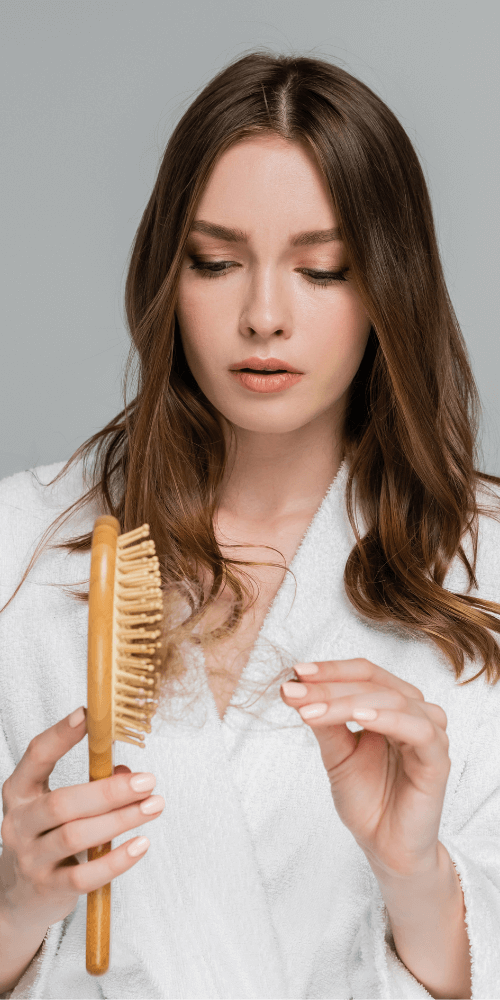

-
Androgenetic alopecia: Also known as chronic hair loss, this common form of baldness is caused by a genetic predisposition and the influence of androgen hormones. Male pattern hair loss typically begins with gradual thinning at the hairline, temples, and crown. Around 50% of men experience it by age 50, with the risk increasing over time (1). While less frequent in women, it can occur as diffuse thinning focused on the top of the scalp.
-
Telogen effluvium: A form of diffuse hair loss often triggered by emotional shock, nutritional deficiencies, or periods of high stress. This condition can affect anyone and is typically temporary. It is commonly identified by excessive hair shedding on the brush, pillow, or floor—a sign of disrupted and accelerated hair growth cycles (2).
-
Alopecia areata: Alopecia areata is characterized by patchy hair loss, which can vary in size and typically appears on the scalp, eyebrows, or beard. It often manifests as sudden, handfuls of hair falling out, which can be particularly alarming. This condition results from an autoimmune disorder where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles, leading to hair loss. While it most commonly affects children and teenagers, alopecia areata can occur at any age. (3)
-
Scarring alopecia: A permanent form of hair loss resulting from damage to the scalp that destroys the hair follicles. It can be caused by severe infections, chronic inflammation, burns, or certain skin conditions. Once the follicles are destroyed, hair regrowth is no longer possible.
-
Ringworm: A contagious fungal infection of the scalp that causes round, hairless patches and scalp irritation. Ringworm is more common in children but can affect people of all ages.
-
Lichen planus: A chronic inflammatory condition that can affect the skin, nails, mouth, and scalp. When it impacts the scalp (lichen planopilaris), it may lead to scarring alopecia and result in permanent hair loss if left untreated.
2. Hormonal Changes and Their Impact on Hair Loss
Hormones play a fundamental role in maintaining healthy hair, and hormonal imbalances can lead to excessive hair loss. In women, specific life stages—such as pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause—are frequently associated with hormonal fluctuations that affect hair growth and shedding.
-
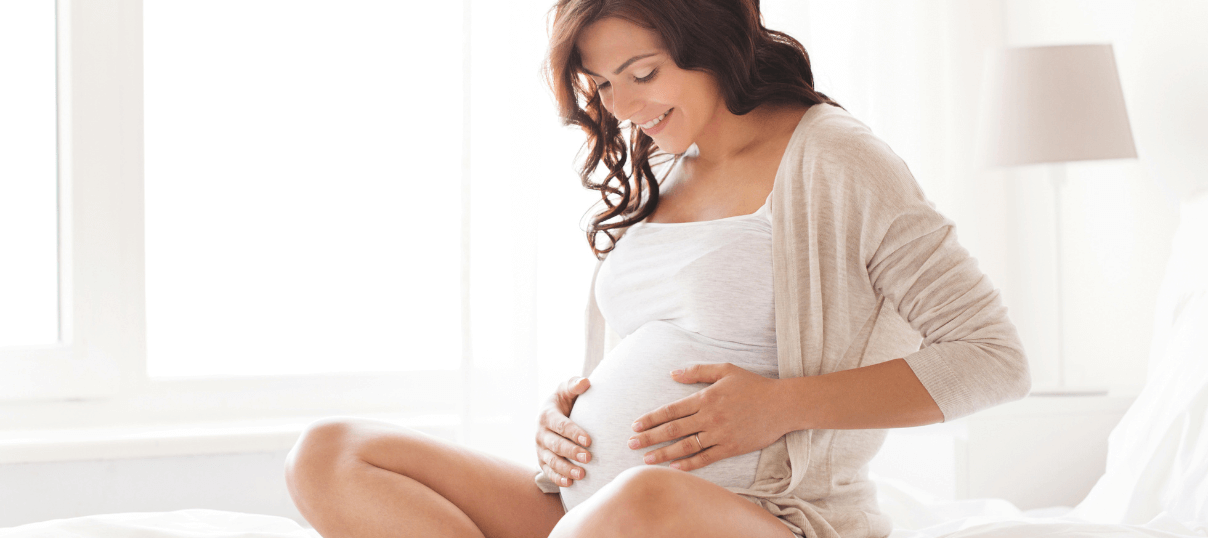
Pregnancy and postpartum: During pregnancy, rising estrogen levels slow down the natural hair shedding cycle, making hair appear fuller and thicker. However, after childbirth, estrogen levels drop sharply, leading to noticeable hair loss. This temporary condition is known as postpartum hair loss or postpartum telogen effluvium (4).
-
Menopause: During menopause, the decline in female hormones such as estrogen and progesterone can cause a reduction in hair density. Women may experience thinning hair, increased brittleness, and more frequent shedding. This condition, known as Female Pattern Hair Loss (FPHL), is the female counterpart to androgenetic alopecia in men and reflects a hormonal imbalance that directly affects hair follicles (5).

3. The Role of Stress in Hair Loss
Stress—whether emotional or physical—is a leading cause of temporary hair loss. It disrupts the natural hair growth cycle by pushing more hair follicles into the telogen phase, the shedding stage. This condition, known as telogen effluvium, may be triggered or worsened by events such as physical trauma, surgery, severe illness, or emotional shock.
Prolonged or chronic stress can result in diffuse hair thinning, which often becomes noticeable several months after the triggering event. The good news is that this type of hair loss is typically reversible once stress levels are reduced and the body regains its natural balance (6).
The Different Forms of Hair Loss
Hair loss can present in various forms depending on its cause and severity. Localized hair loss often appears in patches, as seen in alopecia areata, while diffuse thinning affects the entire scalp and is commonly linked to factors such as stress or hormonal imbalance.
In some cases, temporary hair loss occurs due to triggers like nutritional deficiencies or emotional trauma, with hair typically regrowing once the underlying issue is resolved.
Conversely, permanent hair loss, such as androgenetic alopecia, is marked by a gradual reduction in hair density, especially on the crown and top of the head. Over time, the hair progressively miniaturizes until follicles stop producing new hair if left untreated.
Choosing the right treatment based on the type of hair loss is crucial to promote hair regrowth and slow down further shedding.
Solutions for Hair Loss – Treatments
When facing hair loss, there are several effective solutions available—from targeted hair care treatments and nutritional supplements to healthy lifestyle habits. These approaches can help reduce hair shedding, support hair regrowth, and improve overall scalp health.

1. Dietary Supplements to Strengthen Hair from Within
Dietary supplements offer an effective way to nourish hair from the inside and correct potential nutritional deficiencies that contribute to hair loss. By supplying essential vitamins, minerals, and amino acids, they help fortify hair strands, improve structure, and stimulate healthy, lasting hair regrowth.
Discover Cystiphane Fort, a supplement designed to restore strength and vitality to the hair, and Cystiphane Anagen, specially formulated to boost hair growth in cases of chronic hair loss due to aging or genetic factors.
2. Anti-Hair Loss Shampoos to Slow Shedding and Strengthen Hair
Anti-hair loss shampoos act directly on the scalp and hair follicles to reinforce the hair at its root and reduce excessive shedding. These treatments are enriched with active ingredients that stimulate microcirculation, enhance follicle health, and promote hair density, all while leaving the hair soft, shiny, and more resilient.
Discover Cystiphane Anti-Hair Loss Shampoo, ideal for managing occasional or chronic hair loss. It works from the roots to slow down shedding and visibly improve hair thickness and vitality.
3. Anti-Hair Loss Lotions to Stimulate Hair Regrowth
Hair lotions are also an effective option to combat hair loss. By stimulating blood circulation in the scalp and strengthening hair follicles, they promote hair regrowth. They are particularly recommended for treating chronic or occasional hair loss.
Try Cystiphane Anti-Hair Loss Lotion, suitable for both men and women, to slow hair loss while stimulating growth.
4. Prescription Medications to Treat Hair Loss
For more advanced or persistent cases of hair loss, dermatologists may prescribe specific medical treatments. These solutions, available in topical or oral form, aim to slow hair thinning, stimulate hair regrowth, and preserve overall hair density. Ongoing medical supervision is essential to monitor results and manage any potential side effects (7).
5. Advanced Techniques to Stimulate Regrowth
As a complement or alternative to conventional treatments, advanced procedures such as PRP therapy (Platelet-Rich Plasma) and low-level laser therapy (LLLT) offer promising results.
PRP therapy uses growth factors from your own blood to activate dormant hair follicles and boost regrowth naturally.
Laser therapy uses low-level LED light to improve scalp microcirculation and reinforce the follicle’s anchoring capacity.
These non-invasive methods are suitable for moderate or chronic hair loss and generally require multiple sessions to achieve optimal results.
For more severe or advanced stages, hair transplantation remains a long-lasting and effective—though more invasive—solution to restore lost hair density.
6. Natural Anti-Hair Loss Treatments for Women and Men
In addition to supplements and specialized hair care, adopting a healthy lifestyle and natural approaches can help prevent and slow down hair loss for both women and men:
- Scalp massages: Regular massages stimulate blood flow to the scalp, enhancing the delivery of nutrients to the hair follicles. Natural oils like castor oil are rich in fatty acids and promote stronger, healthier hair growth.
- Essential oils: Certain oils such as rosemary and lavender have properties that may stimulate hair growth and improve scalp health.
- Balanced diet: Include foods rich in proteins, omega-3 fatty acids, and key vitamins (A, C, D, E) to support optimal hair and scalp health.
Consult a Professional If in Doubt
If hair loss persists despite the use of hair care products, supplements, or natural treatments, it is strongly recommended to consult a dermatologist or a hair specialist. A professional diagnosis can accurately determine the underlying cause of hair loss and guide you toward the most appropriate and effective treatment plan. In cases of chronic conditions like androgenetic alopecia, targeted medical solutions may be necessary to slow down progression and support hair regrowth.
FAQ – Everything You Need to Know About Hair Loss in Men and Women
1. How does hair grow? What are the growth cycles?
Hair growth follows a three-phase cycle:
- Anagen phase: the active growth phase, lasting between 2 and 6 years.
- Catagen phase: a short transitional phase that lasts about 2 to 3 weeks.
- Telogen phase: the resting phase, lasting around 3 months, after which the hair naturally falls out and is replaced by a new one.
This continuous cycle ensures the renewal of hair throughout your life.
2. Does wearing caps or hats accelerate hair loss?
Myth: Wearing hats or caps does not cause hair loss. However, excessively tight headwear may lead to friction and breakage of hair fibers, but it is not responsible for hair thinning or follicle damage.
3. Is fatigue one of the causes of hair loss?
Yes. Chronic fatigue—especially when combined with stress—can disrupt hormonal balance and weaken hair growth. This can result in telogen effluvium, a type of temporary hair loss often triggered by physical or emotional strain.
References
(1) Severi G, Sinclair R, Hopper JL, English DR, McCredie MR, Boyle P, Giles GG. Androgenetic alopecia in men aged 40-69 years: prevalence and risk factors. Br J Dermatol. 2003 Dec;149(6):1207-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2003.05565.x.
(2) Asghar F, Shamim N, Farooque U, Sheikh H, Aqeel R. Telogen Effluvium: A Review of the Literature. Cureus. 2020 May 27;12(5):e8320. doi: 10.7759/cureus.8320.
(3) Dainichi T, Iwata M, Kaku Y. Alopecia areata: What's new in the epidemiology, comorbidities, and pathogenesis? J Dermatol Sci. 2023 Dec;112(3):120-127. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2023.09.008. Epub 2023 Oct 11.
(4) Gizlenti S, Ekmekci TR. The changes in the hair cycle during gestation and the post-partum period. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014 Jul;28(7):878-81. doi: 10.1111/jdv.12188.
(5) Bertoli MJ, Sadoughifar R, Schwartz RA, Lotti TM, Janniger CK. Female pattern hair loss: A comprehensive review. Dermatol Ther. 2020 Nov;33(6):e14055. doi: 10.1111/dth.14055.
(6) Thom E. Stress and the Hair Growth Cycle: Cortisol-Induced Hair Growth Disruption. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016 Aug 1;15(8):1001-4.
(7) Kanti V, Messenger A, Dobos G, Reygagne P, Finner A, Blumeyer A, Trakatelli M, Tosti A, Del Marmol V, Piraccini BM, Nast A, Blume-Peytavi U. Evidence-based (S3) guideline for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia in women and in men - short version. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018 Jan;32(1):11-22. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14624.