WHAT IS CANDIDIASIS?
IT IS A YEAST
Candidiasis is classified within fungal infections, representing a group of conditions caused by the excessive growth of Candida yeast.
This overgrowth can lead to several types of candidiasis, each associated with specific symptoms and requiring tailored approaches for prevention and treatment.
DIFFERENT LOCATIONS
• VAGINAL CANDIDIASIS:
Includes itching, redness, discomfort during sex, burning upon urination, and a white discharge.
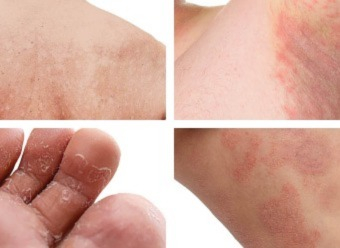
• CUTANEOUS CANDIDIASIS:
Causes rashes in warm, moist areas with redness and itching.
• ORAL CANDIDIASIS (THRUSH):
Features white mouth lesions, pain, and swallowing difficulties.
RISK FACTORS AND CAUSES
The risk factors and causes of candidiasis revolve around conditions that disrupt the natural balance of yeast and bacteria, leading to yeast overgrowth.
These risk factors include:
• Medication Effects: Antibiotics can disrupt microbial balance, fostering yeast.
• Hormonal Shifts: Elevated estrogen and other hormonal changes may encourage yeast growth.
• Health Status: Diabetes and weakened immunity elevate infection risk.
• Environmental Factors: Yeast flourishes in warm, moist conditions.
DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT AND PREVENTION
Diagnosing candidiasis typically involves a physical examination, lab cultures, or microscopy to identify yeast presence.
Treatment may involve topical therapies or oral antifungals, depending on the infection's location and severity.
Preventing candidiasis focuses on maintaining a balance of yeast and bacteria in the body and keeping potential infection sites clean and dry.
Here are strategies to prevent candidiasis:
• Hygiene: Clean and dry feet, regular bathing, and fresh clothes help inhibit yeast.
• Clothing Choices: Opt for natural fabrics like cotton to minimize moisture.
• Dietary Adjustments: Reduce intake of refined sugars and yeasts.
• Blood Sugar Management: Especially important for diabetics to prevent infections.
• Prudent Medication: Use antibiotics or steroids with caution, only when necessary.
• Stress Control: Manage stress to bolster immunity against Candida.
By understanding the signs, treatments, and preventive measures for candidiasis, individuals can better manage their health and prevent recurrence of this common infection.
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2024) 'Candidiasis Basics', Candidiasis. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/candidiasis/about/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/diseases/candidiasis/index.html
2. WebMD. (2024) 'What is Candidiasis (Yeast Infection)?', WebMD. Available at: https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/what-is-candidiasis-yeast-infection.
3. Medscape. (2024) 'Candidiasis Overview', Medscape. Available at: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/213853-overview?form=fpf